
IVF Surrogacy : In Vitro Fertilization Process, PGD Testing
Introduction
IVF has changed how families build their future. Today, many people turn to IVF and surrogacy when natural conception is not possible. If you are researching IVF surrogacy or trying to understand surrogacy in vitro fertilization, you may feel overwhelmed by medical terms, testing options, and possible risks.
This article explains the IVF surrogacy process in clear, simple language. You will learn the gestational carrier meaning, how a PGD test works, what doctors mean by nonviable pregnancy, and why topics like cord blood and hormone changes matter after pregnancy.
What Is IVF Surrogacy
IVF surrogacy combines in vitro fertilization with the help of a gestational carrier. Doctors create embryos in a laboratory using IVF. They then transfer one embryo into the uterus of a surrogate who carries the pregnancy.
People often use IVF surrogacy when pregnancy is medically unsafe, when repeated IVF cycles fail, or when same sex couples or single parents want to build a family.
When you see the phrase surrogacy in vitro fertilization, it simply describes this medical and reproductive partnership.
Gestational Carrier Meaning
Many people ask what gestational carrier means and how it applies to IVF.
A gestational carrier is a woman who carries a pregnancy created through IVF but has no genetic connection to the baby. The embryo comes from the intended parents or from donors.
Understanding the gestational carrier meaning helps families feel more confident and informed as they move through the IVF surrogacy process.
The IVF and Surrogacy Process Step by Step
The IVF surrogacy journey usually includes the following stages:
1. Fertility testing and medical evaluations
2. Ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval
3. Fertilization of eggs in the laboratory
4. Embryo development and monitoring
5. Genetic screening when recommended
6. Embryo transfer to the gestational carrier
7. Pregnancy monitoring and prenatal care
Each step plays an important role in improving success rates and supporting a healthy pregnancy.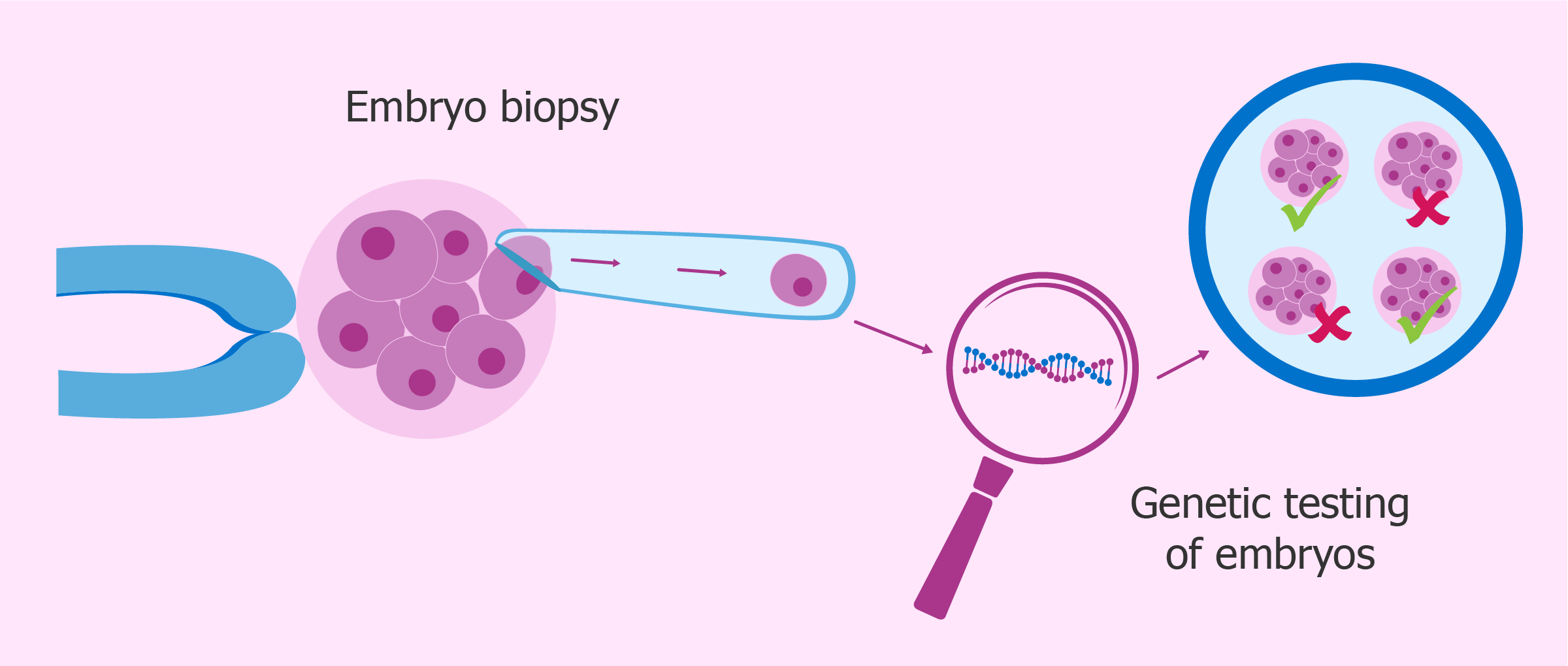
PGD Test Explained
A PGD test is a genetic screening method used during IVF. Many people search for PGD means or the PGD medical abbreviation, which stands for Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis.
Doctors use PGD to check embryos for certain genetic conditions or chromosomal abnormalities before transfer. This allows the medical team to select embryos with the strongest potential for healthy development.
PGD does not guarantee pregnancy success, but it helps reduce specific genetic risks in IVF surrogacy.
Hormone Problems After Pregnancy
Some women experience hormone problems after pregnancy, including mood changes, fatigue, or temporary cycle irregularities. These changes can affect gestational carriers as well.
Medical teams monitor hormone levels during IVF surrogacy and after delivery. Follow up care, rest, and emotional support help the body return to balance over time.
Understanding hormonal recovery helps intended parents and surrogates feel prepared for the postpartum phase.
Define Cord Blood and Why It Matters
Many families ask doctors to define cord blood during IVF planning. Cord blood contains stem cells collected from the umbilical cord after birth.
Some families choose to store cord blood for potential future medical use. Others donate it to public banks. While optional, learning about cord blood early allows families to make informed decisions before delivery.
FAQ
What does gestational carrier mean in IVF surrogacy
A gestational carrier carries a pregnancy created through IVF and does not share genetic material with the baby.
What does PGD mean in IVF
PGD means Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis. It screens embryos for genetic conditions before embryo transfer.
What is a nonviable pregnancy in IVF
A nonviable pregnancy refers to a pregnancy that cannot develop into a live birth, often due to chromosomal or early developmental issues.
Conclusion
IVF surrogacy combines medical science with careful planning and collaboration. By understanding IVF steps, PGD testing, gestational carrier roles, and recovery considerations, families can approach the process with greater clarity and confidence.
Clear information supports better decisions. With proper guidance and medical care, IVF surrogacy continues to help families grow in meaningful ways.
